Staking on Stader & Liquidity Providing on QuickSwap
Key Takeaways:
- This strategy fits the profile of an investor who is willing to take on some risk in exchange for an attractive reward.
- The strategy leverages on two protocols: Stader for MATIC liquid stalking and QuickSwap for liquidity providing
- The strategy is fairly simple but involves some steps: on the Polygon chain, half of the MATIC tokens are swapped into MaticX by staking them in Stader. These tokens are then deposited in the QuickSwap pool in order to provide liquidity to the MaticX/MATIC pool. Two tokens and two protocols are involved.
- The Yield (APY) is composed of
- Stader staking of MATIC
- Liquidity providing in QuickSwap, MaticX/MATIC pool
- Protocol incentives - Given the limited TVL of the QuickSwap pool, even a 1m MATIC strategy cap could negatively impact the currently offered APY (scalability risk).
- A material part of the Annual Percentage Yield (APY) comes from farming/staking rewards. These rewards are subsidised by the protocol and may not be fully sustainable in the future (yield sustainability risk). A lockup period of 30 days means that in case of adverse market conditions the strategy cannot be exited immediately (lockup risk).
- Staking and Liquidity Providing are subject to very specific risks, namely slashing and impermanent loss. Stader is a trustable protocol (low slashing risk) and the fact that MaticX is backed 1-1 by staked MATIC tokens redeemable at any time should ensure that the pair is always trading close to parity (low IL risk).
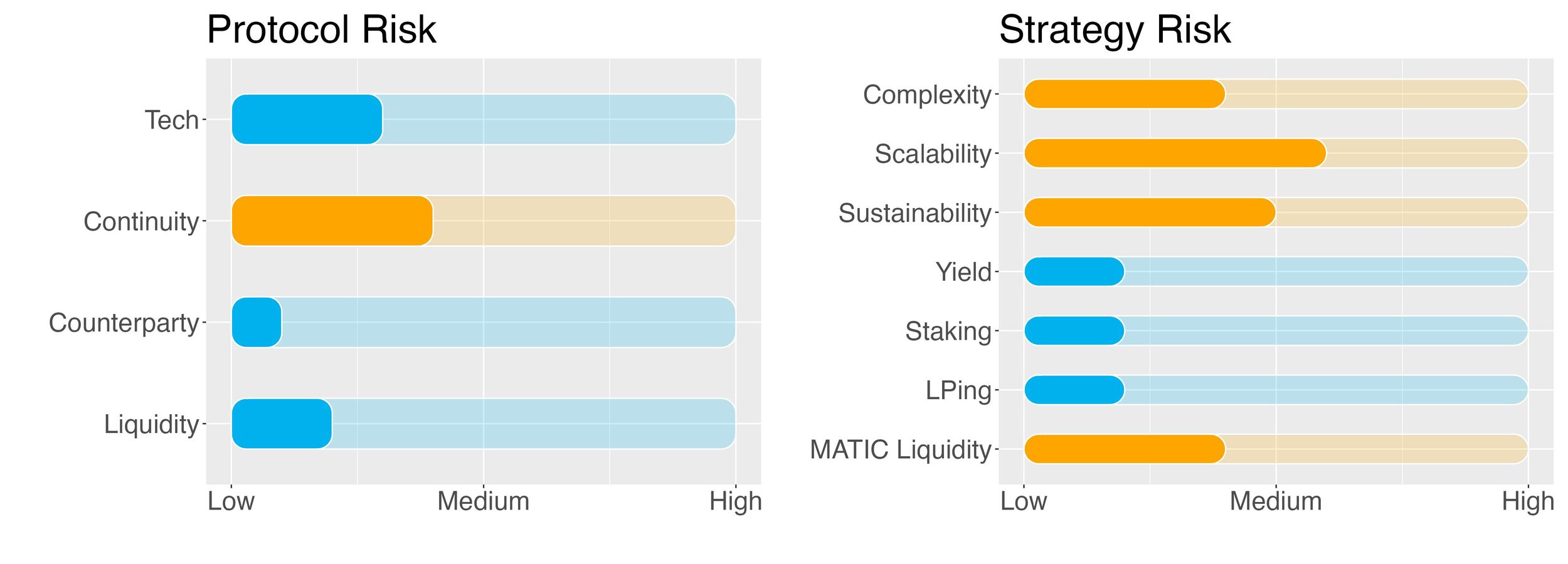
- Risk Checklist: in our view the predominant risks for this strategy are
- Tech risk
- Sustainability risk
- Complexity risk
- Liquidity risk
1. Strategy Explained
The strategy stakes half of the MATIC token Stader in return for MaticX. Then the MaticX and MATIC tokens are deposited in a QuickSwap pool and farmed. The strategy runs on the Polygon chain.
Lockup period: 30 days.
2. Strategy Risks
Trust Score
Stader Labs is a non-custodial innovative contract-based staking platform that helps users conveniently discover and access staking solutions.
The protocol went live in December 2021 and displays a TVL of around $140m.
SwissBorg trust score for Stader is ‘green’, i.e. the protocol is trustable.
The score value is 70% signalling that the protocol is reliable.
QuickSwap is a permissionless Ethereum-based DEX (decentralised exchange) that runs on Polygon Network's layer 2 infrastructure. QuickSwap is a fork of Uniswap that employs the automated market maker (AMM) approach for token trading. The protocol was launched in early 2021.
SwissBorg trust score for QuickSwao is ‘green’, i.e. the protocol is trustable. The score value is 85%.
Protocol Risks
Project Continuity Risk
Project continuity risk is medium to low.
Stader displays a TVL $150m. This puts it in the top 10 staking protocols. The difference with the largest staking protocol, Lido, is however abysmal with Lido having over $9b locked in.
To assess the sentiment around Stader we look at its token price and volatility, as well as at the Google Trend for the last 30 and 90 days. Overall sentiment is medium.
Stader continuity risk is set to 3/10.
QuickSwap is in the top 50 DeFi protocols in terms of TVL with a value of around $180m. Within its ‘DEX’ category, the exchange sits just outside the top 10 but within the Polygon network it is the largest DEX. Compared to top DEXes like UniSwap and Curve QuickSwap display a rather limited market share by trading volume (less than 1%). In terms of valuation the token market capitalization to its TVL is 0.20, in front of a median for the category of 0.87. Overall sentiment is good.
QuickSwap continuity risk is 5/10.
Counterparty Risk
Counterparty risk is deemed low.
Counterparty risk exists whenever an asset is handed over to an external provider. Any credit events involving the staking provider could affect the assets that have been entrusted to them.
That said, staking via a 3rd party is fundamentally different from depositing funds into a lending protocol that later becomes insolvent.
We seek to select only trustable staking providers in order to minimise counterparty risk.
Stader places utmost importance to ensure users' funds are staked with the best-in-class validators in the ecosystem. In order to be considered for Stader pools, validators need to meet threshold performance criteria (e.g. on up-time).
Each pool has a unique characteristic based on which validators are selected for that particular pool. In the long run Stader would select the validators programmatically and rebalance delegations based on performance filters. Additionally, as the Stader platform is decentralised, governance will determine validator selection criteria, policies, and so on.
Last, a Slashing Insurance will be provided by validators via the Stader tokens staked.
QuickSwap is an automated market maker (AMM). It is fully decentralised and its operations are all regulated by smart contracts. There is hence no counterparty credit risk when providing liquidity to a pool in the protocol.
Counterparty risk is 2/10.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk is deemed low.
Funds held by the staking provider are redeemable at any time (according to the technical lockup period).
The LP position can be exited without the need of any lockup.
Liquidity risk is 1/10.
Strategy Risks
Complexity
Complexity of strategy is medium.
The strategy employs one chain (Polygon), 2 protocols (Stader and QuickSwap), and two tokens (MATIC and MaticX). Because of this the complexity risk of the strategy is deemed medium.
Complexity of the strategy is 4/10.
Scalability
Scalability risk of the strategy is medium to high.
Staking is a highly scalable practice. Indeed, the more stakers are participating, the higher the safety of the blockchain.
With respect to the farming leg of the strategy, the QuickSwap MATIC/MaticX farming pool displays a TVL of around $3.8m, and the strategy will be capped at 1 million MATIC. Therefore there is the risk that the SwissBorg position represents a material part of this vault. This could negatively impact the offered APY.
Scalability risk of the strategy is 6/10.
Sustainability
Sustainability risk of strategy is medium.
The strategy generates yield via MATIC staking in Stader (i.e. taking part in the Polygon network Proof-of-Stake algorithm) and by providing liquidity to the MATIC/MaticX pool in QuickSwap (i.e. collecting the trading fees).
The yield obtained from the staking leg is sustainable as it comes from participating in the validation of Polygon transactions, the Proof-of-Stake mechanism.
A material part of the APY is however boosted by Stader and QuickSwap and paid out in their own token. Because of these incentives, the sustainability of the offered APY could not be guaranteed in the long term (obviously, if e.g. QuickSwap trading volumes were to increase this would change).
Sustainability risk of the strategy is conservatively set to 5/10.
Yield Risk
Yield risk of strategy is low.
Staking provides a constant stream of income with low variability. In addition, thanks to the protocol incentives (see Sustainability risk above) the final APY is not expected to show much volatility.
Yield risk of the strategy is 2/10.
Stader Staking Risks
Stader staking risk is deemed low.
Polygon is a PoS network, enabling crypto investors to stake Polygon (MATIC) to contribute to network security and decentralisation and earn an attractive yield for their staked tokens. Polygon relies on a set of validators, who stake their MATIC tokens as collateral to secure the network and earn rewards in exchange for their service. Validators run a full node, produce new blocks, participate in consensus, validate transactions, and earn rewards for performing network operations. To become a validator, one needs to stake MATIC tokens with staking management contracts on the Ethereum mainnet.
A validator node receives inflation-funded block rewards and network-based transaction fees in return for good validator performance. Rewards are distributed to all stakers proportional to their stake at every checkpoint. However, slashing staked funds are placed at risk and can be penalised or slashed if a validator node commits a malicious act like double signing or validator downtime.
Liquid staking providers like Stader enables investors to participate indirectly in staking by delegating their tokens to a validator. Validators charge a fee for running a service for delegators. While delegators share rewards with their validators, they also share the risks of slashing. To minimise the risk of slashing, Stader carefully selects and monitors validators data on a real time basis with internal alerts and monitoring. In the event of an increased performance / slashing risk on the validators, a validator is proactively replaced and the stake is redelegate across the rest of the validators in the pool.
Slashing risk for the strategy is 2/10.
QuickSwap Liquidity Providing Risks
Liquidity Providing risk is deemed low.
The strategy converts part of the MATIC into MaticX in order to enter the QuickSwap liquidity pool. MaticX is expected to trade higher than MATIC since it accrues the staking APY and gives the right to receive a constantly increasing number of MATIC at redemption.
In the event of a heavy depeg of MaticX (could be caused by issues with the Stader smart contracts, security and key management, or a slashing event in which staked MATIC are lost) the QuickSwap pool would likely be drained out of MATIC by investors dumping MaticX.
In this case the LPer would incur in impermanent loss (IL) since in order to exit the position he will be left with the lower values token.
Additionally, an exploit on the QuickSwap pool could also put pressure on the peg.
These events are more relevant from a tech point of view and these risks have been covered in the Trust Score section.
In terms of IL it is however unlikely that MaticX price deviates substantially from that of MATIC: one can always unstake the Stader position (though with a 9-day unstaking delay window) and get back MATIC. There could be a liquidity premium attached to the MaticX value but this will not likely materially impact the peg.
The risk of providing liquidity is 2/10.
Liquidity Risks of staking
Liquidity Risk on staking MATIC is medium.
Liquid staking on Stader plus QuickSwap liquidity providing requires the investor to lock-up their MATIC tokens for a period of 30 days. Regardless of the direction the market chooses during this time, your assets will be out of reach. This aspect needs to be carefully considered when entering this strategy.
Liquidity risk is therefore set to 4/10.
3. Conclusions/Recommendations
Liquid staking per se is generally considered a very safe investment. Stader, the chosen liquid staking protocol, has been reviewed and approved by the SwissBorg tech team. The offered yield is enhanced by providing liquidity to the MATIC/MaticX pool on QuickSwap. This introduces some additional risks.
When it comes to the ‘real’ APY, the yield currently provided to users comes from staking and liquidity providing fees, as well as from protocol incentives.
The investment strategy is fairly simple but yet it requires some understanding of how DeFi operates. It does involve a 30-day locking period, and rewards are paid out daily.
The SwissBorg Risk Team ranks MATIC on Stader/QuickSwap as a Satellite investment, one for an investor with a medium understanding of DeFi and yielding, who is willing to take on some risk in exchange for an interesting reward on MATIC.
Try the SwissBorg Earn today!





